
Advancing international comparative research on the roles of teaching assistants in schools
Despite the growing number of teaching assistants (TAs) in schools worldwide, comparative international research on their roles remains limited. Most are small-scale qualitative inquiries involving just two or three countries. While cross-country summaries exist, they are usually descriptive rather than systematic, making meaningful comparison difficult. One major barrier has been the absence of a shared framework for collecting and analysing data on TAs at scale.
That is where the International Teaching Assistant Research Network (ITARN) comes in. Formed in response to an EERA blog calling for wider collaboration in this field, our network has developed the Comparative Framework on TAs (CoFTA). This draft framework is designed to structure the collection and analysis of comparative data about TAs and their roles in schools.
Members of ITARN presented the framework for the first time at a symposium at the European Conference on Educational Research (ECER) in Belgrade in September [1]. The focus was on the formal and informal roles of TAs across five major education systems: the US, England, Shanghai (China), Germany, and Ireland.
Each paper explored how policies and wider forces shape both the intended and the actual work of TAs in practice. The final paper brought these perspectives together, highlighting key similarities and differences across the contexts, and identifying the contextual factors and drivers that explain the misalignment between TAs’ formal role and their enacted role.
Six factors shaping TA roles
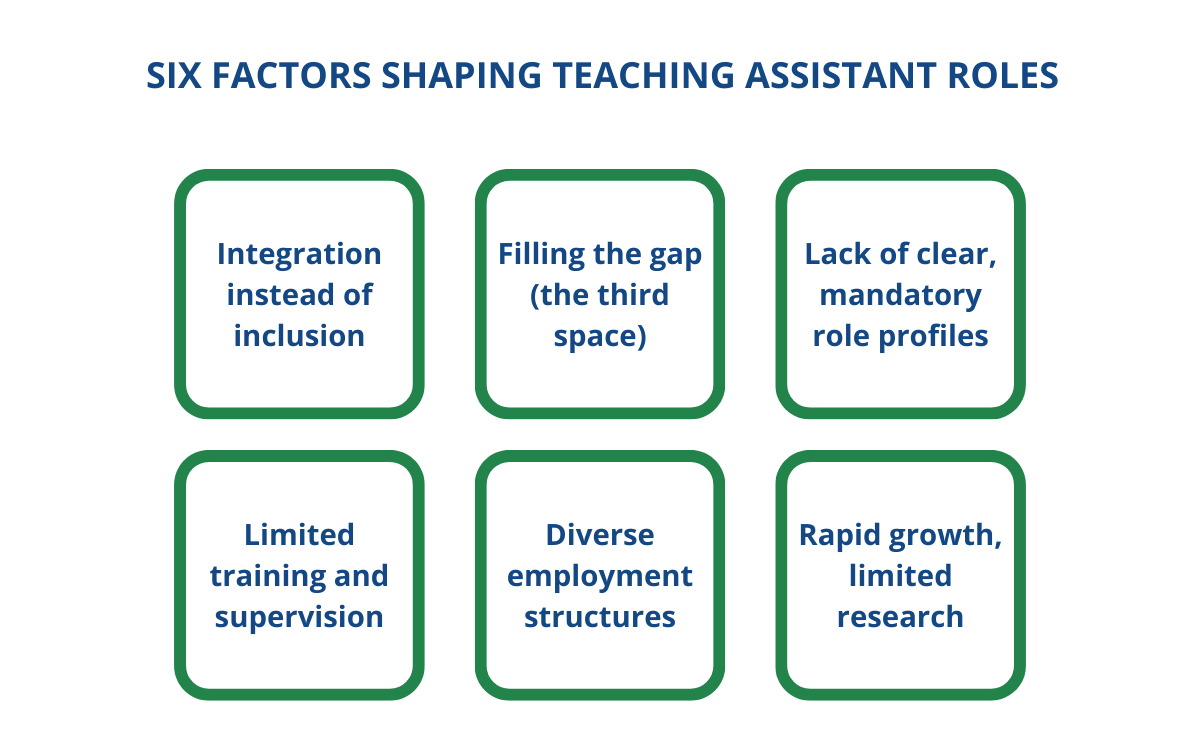
- Integration instead of inclusion. Too often, students with special educational needs (SEN) are expected to adapt to existing systems and processes, with TAs supporting them to ‘fit in’ rather than schools adapting to their needs. In each country context, TAs are viewed as pivotal to the educational and social inclusion of students with SEN. Yet at the same time, the high amounts of high intensity support these students receive from TAs cuts across and replaces time with teachers and peers, creating (unintentional) barriers to a more authentic model of inclusion.
- Filling the gap (or the ‘third space’). TAs are frequently deployed reactively, stepping in where there are shortages of teachers, special educators, or therapeutic support. This places them in a ‘third space’ between care and education. There are concerns where these roles overlap or stray into the jurisdiction/responsibility of professionals. For example, in Ireland, where TAs are not qualified or trained in providing emotional support to emotionally-vulnerable students; and in England, where TAs are deployed to cover classes and lead lessons because schools are short on teachers.
- Lack of clear role profiles. Few countries have up-to-date national policies that define TAs’ formal responsibilities. Those that do can be advisory, not mandatory. This lack of clarity not only helps explain the occupation of ‘third spaces’, but also the ways in which TAs interact with students in ways that, while well-meaning, are ultimately unhelpful. For instance, in Germany, TAs’ tendency to scribe and organise materials can erode, rather than build, students’ independence.
- Limited training and supervision. Possibly connected to the lack of role clarity, there is also a widespread lack of evidence-based guidance and training for TAs. However, practical guidance, which incorporates training and advice on deploying TAs to support student independence, does exist in England.
- Employment structures. TA employment patterns varies widely. In England, Ireland, and the US, TAs are employed by schools and part of the school system/workforce. While in Germany, TAs are employed by welfare organisations, and in China, often by the parents of children with SEN.
- Rapid growth, limited research. The number of TAs worldwide has grown – and continues to grow – substantially. While there is relatively more research in England, overall, research is patchy. There is vanishingly little large-scale work at the national level, let alone the international level. Also, perspectives from the global south are underrepresented.
What’s next for ITARN
The ECER symposium is just the start. ITARN is now preparing its first written outputs (including on CoFTA), bringing together the symposium papers and new contributions from a wider range of countries, including the global south. Our aim is to publish a collection that compares and contrasts international evidence and perspectives, and reflects on how social and cultural contexts shape TA roles.
Alongside this, we will continue to develop the CoFTA framework. Future work will expand its scope to include TA education and training, employment conditions, and school-level processes, such as planning, feedback, staff integration, and professional belonging.
Teaching assistants play a critical role in education systems around the world. By developing common tools for comparison and creating space for new and diverse voices, ITARN is helping to move the field forward. The work begun at ECER 2025 marks an important step toward building a truly international understanding of the TA role.
We welcome new members! If you’d like to join ITARN, or learn more about our work, please email Run Tan at r.tan@rug.nl.
Key Messages
-
International understanding of teaching assistant roles is fragmented, and the newly formed International Teaching Assistant Research Network (ITARN) is addressing this by creating a shared comparative framework to unify global research efforts.
-
Across countries, teaching assistants often take on complex responsibilities shaped by policy gaps, workforce shortages, and differing interpretations of inclusion.
-
There is a persistent mismatch between how education systems intend TAs to work and the realities of their day-to-day practice, influenced by cultural, organisational, and structural factors.
-
The rapid expansion of the TA workforce contrasts with the limited scale and scope of existing research, underscoring the need for more systematic and internationally diverse evidence.
-
ITARN’s ongoing work aims to build a more coherent global picture of TA roles, enabling policymakers, researchers, and school leaders to develop more effective, equitable, and evidence-informed approaches.

Dr Rob Webster
Associate Professor at UCL Institute of Education, UK
Dr Rob Webster is an Associate Professor at UCL Institute of Education, UK. He was part of the research team that conducted the world’s largest study of teaching assistants: the ground-breaking Deployment and Impact of Support Staff project. Rob writes extensively on the role of teaching assistants, and he also created the award-winning Maximising the Impact of Teaching Assistants programme for schools (maximisingtas.co.uk). Prior to research, Rob worked as a teaching assistant in mainstream and special schools.
Website: www.rob-webster.com
http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1416-4439

Dr. Run Tan
Faculty of Behavioural and Social Sciences, University of Groningen, The Netherlands
Run Tan is Assistant Professor in inclusive and special needs education at the Faculty of Behavioural and Social Sciences in Groningen University, Netherlands. Guided by critical disability theory and cultural–historical framework, she conducts cross-cultural comparative studies to understand how inclusion takes place and how to sustain and maximize it, while bringing in the voice of the Global South. While positing children’s voice in the centre, she critically examines three key stakeholders (teachers’, teaching assistants’ and families’) agency (attitude, self-efficacy) and how their daily practice facilitate inclusion from the main four dimensions of: access, acceptance, participation and achievement.
Uni profile page: https://www.rug.nl/staff/r.tan/?lang=en

Dr. Claire Griffin
Mary Immaculate College, University of Limerick, Ireland
Dr. Claire Griffin is a Chartered Educational Psychologist and Assistant Professor in Educational and Developmental Psychology at Mary Immaculate College, Limerick, Ireland. She is programme leader of the B.Ed in Education and Psychology programme and placement supervisor of trainee Educational Psychologists and trainee teachers. Claire’s PhD research focused on the preparedness and deployment of Special Needs Assistants (SNAs) when supporting pupils’ behavioural care needs and independence development in mainstream primary schools in Ireland. Since graduating, Claire has continued research in this area, with particular interest in evidence-based frameworks and procedures to enhance pupil outcomes. Claire is currently a member of the Steering Group of the SNA Workforce Development Plan in Ireland. She has previously worked on national and regional research projects in Ireland and has been recipient of a range of teaching and research awards.
Uni profile page: https://www.mic.ul.ie/staff/370-claire-griffin
Other blog posts on similar topics:
Note
[1] In addition to the authors of this blog, the following members of the ITARN network presented papers at ECER 2025:
- Prof Dr Bettina Fritzsche, Professor of General Education, University of Education, Freiburg, Germany
- Prof Dr Julia Gasterstädt, University Münster, Germany
- Dr Lindsey Kaler, Postdoctoral Research Associate, Brown University, USA
- Prof Dr Andreas Köpfer, Professor for Research in Inclusive Education, University of Education, Freiburg, Germany



